Plasma gel for dentistry: beauty is in the blood
The use of plasma gel as a filler and biostimulator on the face gains more and more space in Orofacial Harmonization. The use of autologous blood products is a consolidated practice in dentistry, both for the correction of bone and soft tissue defects. However, this resource has also shown great potential as a filling biomaterial for Orofacial Harmonization, configuring a safe and low cost solution.
The use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and plasma rich in platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF) has been showing positive effects in numerous treatments, such as inflammatory, orthopedic, rheumatological and various dental treatments. Products derived from PRP have demonstrated efficacy in tissue regeneration, with modulation of the inflammatory response, induction in the synthesis of collagen and extracellular matrix components, in addition to stimulating local vascularization.
The term “PRP” is often used to characterize a plasma solution obtained from whole blood, with high concentrations of platelets when compared to whole blood. Once platelets are activated, the solution becomes enriched in a wide variety of growth factors, in addition to plasma proteins.
The main element in the PRP of interest in tissue biomodulation applied to aesthetics refers to platelets. Produced in the bone marrow, platelets are the product of the cytoplasmic fragmentation of the megakaryocyte (bone marrow cell) and have approximately 2 micrometers in diameter, with a useful life of seven to ten days.
The main platelet function is to guarantee blood hemostasis. However, scientific studies have shown that platelets contain more than 800 proteins with numerous post-translational modifications, resulting in more than 1,500 protein-based bioactive factors. Among the various platelet properties, we know its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects and the secretion of antimicrobial peptides.
The knowledge of its modulating and stimulating properties for the proliferation of mesenchymal stem cell lines, makes PRP an excellent autologous product as a useful auxiliary element to improve tissue regeneration and promote neocolagenesis. PRP has attracted attention in the aesthetic field as an adjunctive treatment for facial rejuvenation, alopecia and stimulation for tissue renewal.
Some studies focused on restoring tissue integrity have shown the role of platelets in the wound healing process: during the inflammation and coagulation phase, the formation of a blood clot induces adhesion, aggregation and degranulation of circulating platelets. Platelet granules, the content of which is formed by various substances, which are released at the time of activation, promote restoration of tissue integrity. Among the main substances released during platelet activation are growth factors, cytokines, adhesion molecules, interim and proteins that participate in coagulation.
Obtaining platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
Currently, there is a wide variety of protocols for obtaining and preparing the PRP, and all involve the basic preparation steps that initially follow the venipuncture and blood collection, centrifugation, plasma aspiration, a second centrifugation with greater gravitational force, removal of the supernatant and resuspension of the platelet pellet in the residual plasma volume, followed by activation and subsequent application.
Several factors can affect the PRP product, such as temperature, strength and centrifugation time, sequence and number of centrifugations, use of anticoagulation and platelet activation mechanisms, a longer and more vigorous centrifugation sediments the buffy coat layer by reducing platelets in the plasma supernatant , resulting in a lower concentration of growth factors in the final plasma.
Venopuncture: collection in closed system
The processing of human blood to obtain PRP in a closed system (vacuum system) and the manipulation of blood to obtain platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) can be performed in a surgical center or dental office by a duly qualified dentist, in compliance with RDC / Anvisa no 63/2011. The processing of human blood in an open system to obtain PRP for autologous use in Dentistry must be carried out exclusively in Cellular Technology Centers (CTCs), duly licensed by the competent health surveillance under the terms of the current legislation and by agreement between the services by means of written document proving outsourcing. Resolution 158 of the Federal Council of Dentistry, published on June 8, 2015, deals with the use of autologous products considering the need to regulate the use of autologous platelet aggregates for non-transfusion purposes in Dentistry. Check out some highlights of the document:
“… Considering that the Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) is the portion of the blood that contains the platelet components, with the addition of any product, including anticoagulant or coagulant; and considering that Fibrin-Rich in Platelets (PRF) the portion of the blood that contains the platelet components, without adding any product, including anticoagulant or coagulant, resolves:
Article 1 - Recognize and regulate the use of Autologous Platelet Aggregates for exclusively autologous, non-transfusion use in dental practice (Plasma Rich in Platelets and Fibrin Rich in Platelets).
Paragraph 1 - The venipuncture to obtain Autologous Platelet Aggregates for exclusive use in Dentistry by the dentist, duly qualified or by a duly qualified health professional, and co-responsibility with the dentist, is authorized.
- 2 - For the purpose of proving qualification and training in venopuncture to obtain Autologous Platelet Aggregates, diplomas, declarations, certificates and the like may be presented
- 3 - The processing of human blood to obtain Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) in a closed system and the manipulation of blood to obtain Platelet Rich Fibrin (PRF) can be performed in a surgical center or dental office by a dentist. duly qualified, in accordance with RDC / Anvisa no 63/2011 or whatever replaces or complements it.
- 4 - The processing of human blood in an open system, to obtain Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) for autologous use in Dentistry, must be carried out exclusively in Cellular Technology Centers (CTCs), duly licensed by the competent health surveillance under the terms of current legislation and by agreement between the services through a written document that proves outsourcing. ”
Thus, all collection for the use of PRP and its derivatives must be carried out in a vacuum collection system, guaranteeing the sterility of the blood collected. The technique is safe, as it reduces the risk of blood tissue exposure and it is possible to collect considerable volume in a single venipuncture.
This blood collection system has a double bevel needle at both ends, one of which is covered by a rubber cuff that is attached to a tube insertion device, which allows no contact with the blood to occur, and the other end it is exclusively for venipuncture. It is considered venopuncture in an open system when the collection is performed with a syringe and needle, where it is necessary to disconnect the needle to transfer the blood to the collection tube, thus having contact with the environment. The closed system collection allows the biological sample to be processed without any contact of the blood with the external environment using the gravitational force centrifugation method.
To obtain peripheral blood, basilic and cephalic veins are preferably used in the region of the antecubital fossa of the arm, a site with a low risk index associated with venipuncture, such as phlebitis. To perform antisepsis of the puncture site, 70% ethyl alcohol solution is used alone, being an efficient method for decontamination of the region. A tourniquet is used to evidence the vein for venipuncture and release only after filling the first tube to collect peripheral blood, with the tourniquet not being indicated for periods over one minute, in order to reduce potential errors due to prolonged venous stasis - which can change the amount of platelets obtained during venipuncture. The method used for blood collection comprises the vacuum system to maintain blood sterility and obtain the necessary blood in less time to guarantee the physiological proportions of its figured elements. The collection is carried out in 4 mL tubes containing 0.5 mL of 3.8% sodium citrate.
Blood processing
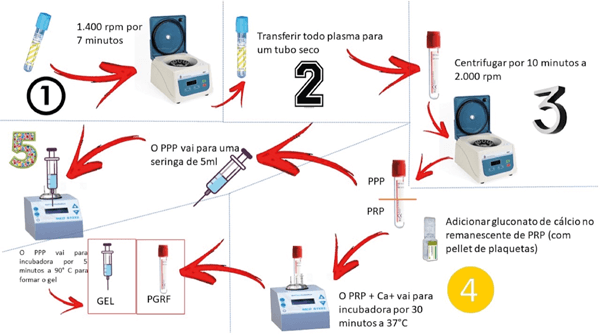
After blood collection, it is segregated into PRP, packed red blood cells and buffy coat, using the modified Ley-Díaz protocol19. An example: 21.6 mL of collected whole blood are distributed in six tubes with a total volume of 3.6 mL, with 3.2% sodium citrate anticoagulant. The tubes are centrifuged in the first cycle for 1,400 rpm at seven minutes, in order to maintain a platelet concentration higher than physiological, and a second centrifugation of 2,000 rpm is performed for ten minutes19.
Description of the technique for obtaining plasma gel
- Venopuncture: obtaining eight tubes of 4 mL of blood - test tube of blue TPA with 3.8% sodium citrate anticoagulant;
- Light blood centrifugation: 1,400 rpm for seven minutes to separate the PRP from the red blood cells;
- Visualization of the “BUFF COAT”: white buffy coat, in white;
- After the first centrifugation, the PRP is aspirated and transferred from the centrifuged tube (yellow part) to a dry 9 ml test tube with a red cap (there is no additional substance in the tube), using a syringe 10 ml;
Second spin: heavier, to separate the poor plasma - 2,000 rpm for ten minutes. This centrifugation promotes the separation between the platelet pellet and the low platelet plasma (PPP), which must be separated for denaturation and the formation of the plasma gel as a filler. The platelet pellet at the bottom of the tube corresponds to the buffy coat;
- A little more than the first half of the tube, after this centrifugation, corresponds to the poor plasma, and is removed in a 10 mL syringe to be used later as a volumizer. The second half of the test tube corresponds to the PRP. Platelets are resuspended, homogenizing manually.
This is followed by the addition of 100 µL of 10% calcium chloride in 1 mL of PRP, with the objective of providing calcium, in order to promote the coagulation cascade and the formation of fibrin;
- The PRP should be incubated at 37º for 30 minutes to promote the formation of the white thrombus and the consequent release of growth factors derived from platelets in the supernatant2020. The serum with growth factors will be the biological inducer for fibroblasts, neocolagenesis and angiogenesis;
- Poor plasma is incubated for five minutes at 90º in the syringe itself. This material is the plasma gel or filler;
- Mix the liquid PRP (10% of the syringe amount) with the gelled PPP (0.8 mL of PRP for each 8 mL of PPP) to control the viscosity of the gel. The quantity is visual. PDGF may or may not be mixed with plasma gel, if it is mixed it provides growth factors.
Formation of plasma gel
For the modification of PPP in plasma gel, we must change some parameters of blood plasma texture, which are obtained by different variables such as temperature, pH and protein concentration, being the best way to maintain the pH characteristics and interaction between proteins, heating with variation from 70ºC to 90ºC. The plasma gel can be described as an intermediate state (Figures 1) between a solution and a precipitate, ensuring the balance between protein-protein and protein-solvent, depending on time and temperature, will promote moisture loss, and its aggregation and protein denaturation starts at 55ºC21.
After separating the PPP in a 5 mL syringe, serial incubations of 37º, 70º and 90ºC are performed for denaturation and gelation of the PPP. The calculation for Spreadability Factor (Fe) corresponds to the relationship between the spreading area achieved with the application of stress on the product. The result is expressed in mm2 / g, considering that a limit effort means the weight in grams of the plates from which the product no longer spreads even when more effort is applied. Thus, this test is based on resistance to forced movement and the results with respect to plasma gel are described in Table 122. The spreadability (Ei) is determined at 25ºC using the equation:
Ei = d2 x π / 4
Considering:
Ei: sample spreadability for weight in square millimeter (mm2).
d: average diameter (mm).
Preparation of plasma gel rich in platelet-derived growth factors
After incubating the PPP for the ideal protein-protein ratio in plasma gel, we enriched the material obtained with PDGF, using a three-way Luer Lock device for transfer to plasma gel, homogenizing the volume of 2 mL of PDGF at 5 mL of plasma gel for subsequent filling in dermal layer23.
Use of plasma gel in Orofacial Harmonization
The most popular injectable facial fillers include hyaluronic acid and bovine collagen. Despite its known advantages, the high cost and the possibility of complications with its application sometimes discourage clinicians and patients from carrying out more extensive procedures with such products. The search for less risky and more cost-effective fillers has stimulated the introduction of autologous implants, including fat and collagen for tissue augmentation and biostimulation. However, these materials demonstrated some problems, such as the morbidity at the donor site and the difficulty in controlling the volume of the acquired tissue.
More convenient, safe and inexpensive autologous materials - such as plasma gel - have been studied with the aim of offering clinically viable and safe filling and biostimulation solutions. In recent years, plasma gel has gained popularity in plastic, orthopedic, oral surgery and several other fields, to overcome autologous fat10. Currently, autologous plasma gel has been used as a dermal filler for aesthetic correction of facial wrinkles and tissue ptosis.
The modification of PPP by the addition of a coagulation cascade activator, such as calcium gluconate 10%, or calcium chloride 10%, thrombin and / or heat treatment, gives rise to a gelatinous material known as “gel plasma "or" plasma gel ". This material contains fibrin - which provides the formula with greater consistency and strength than platelet-rich plasma (liquid PRP). Additionally, the addition of calcium gluconate promotes higher levels of immediate and massive release of growth factors through the formation of the platelet thrombus. Platelets work by degranulating their α-granules, which contain pre-synthesized growth factors. The most potent growth factors are: platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta), insulin growth factor (IGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and growth factor endothelial (EGF). The heating process induces the denaturation of the plasma proteins that keep the gel formula and, subsequently, allows the injection of a precise amount in the desired location.
It is important to note that the gel formula serves as a vehicle for its growth factors added later. The growth factors trapped in the injected plasma gel continue their bioactive action after injection and interact with undifferentiated mesenchymal cells and dermal fibroblasts, binding to their specific cell receptors that promote neo-vascularization and neocolagenesis, resulting in increased tissue soft and reduced wrinkle depth.
The great advantage of Dentistry in relation to other areas of health is the possibility of the practice of venipuncture by dentists who are qualified, in addition to the legalized use of autologous products by the Federal Council of Dentistry. In Medicine and Biomedicine, the use of these products is only allowed experimentally, in research linked to large teaching centers.
Source: Face Magazine. Available at: https://facemagazine.com.br/plasma-gel-a-beleza-esta-no-sangue/. Accesson: 08/24/2020.
